The measurement of Solar Constant.
To effectuate the solar constant measurement we used an instrument, called Bolometer, made of two pipes (one to collect solar beams, the other to point out the sun) and one lead BOLO isolated with POLISTIROLO. The "Instrumental constant" is equal to 17986.6 because the BOLO has mass 24.45 g; the diameter of the exposed face is 1.5 cm and the specific heat of Lead is![]()
During the measurement we calculated, instead of measured, the solar declination degree knowing the COORDINATE of the place and the hour in which the measurements were done. We calculated the air mass with the formula ![]() and having measured a ground power of 212 and 225 W/mē in Florence and 175 W/mē in Lagos, from this results that the solar constant is 636 W/mē, 758 W/mē and 2399 W/mē.
and having measured a ground power of 212 and 225 W/mē in Florence and 175 W/mē in Lagos, from this results that the solar constant is 636 W/mē, 758 W/mē and 2399 W/mē.

We calculated the attenuation factor doing the rapport between the knew value (1371 W/mē) and the one measured by ourselves, obtaining this results: 1,70; 1,49; 0,79. If the measures done in Florence were good, in the one made in lagos was coming up with a problem: with an attenuation factor <1, the atmosphere should be bright and the beams' energy should increase its power approaching to the Earth.

So we realised that the error was in the air mass' measure: ![]() approach well the measure with sufficiently small angles but in Lagos these had a solar declination which is 68°. So we measured a new air mass by means of the triangle in the image
approach well the measure with sufficiently small angles but in Lagos these had a solar declination which is 68°. So we measured a new air mass by means of the triangle in the image
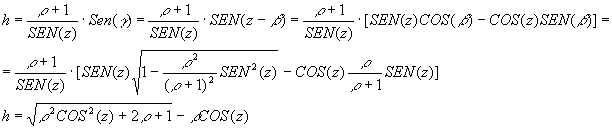
Using this new device we measured again the solar constant and obtained: 624, 726 and 1195 W/mē with the relatives attenuation factors 1,73; 1,54; and 1,07; those are all right and show Lagos' air is cleaner than Florence's one.
![]()